Dabih Documentation
Start using dabih
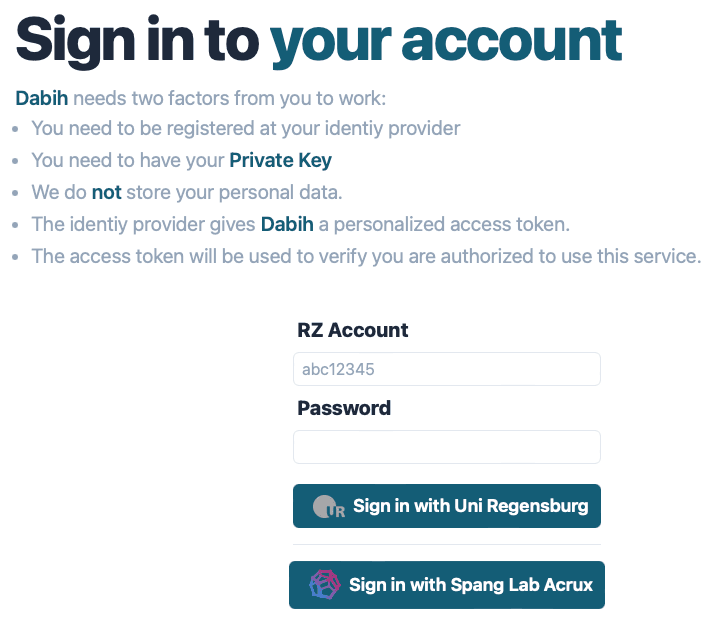
- Sign In to dabih. Account page
- Generate your keypair and upload the public key to dabih.
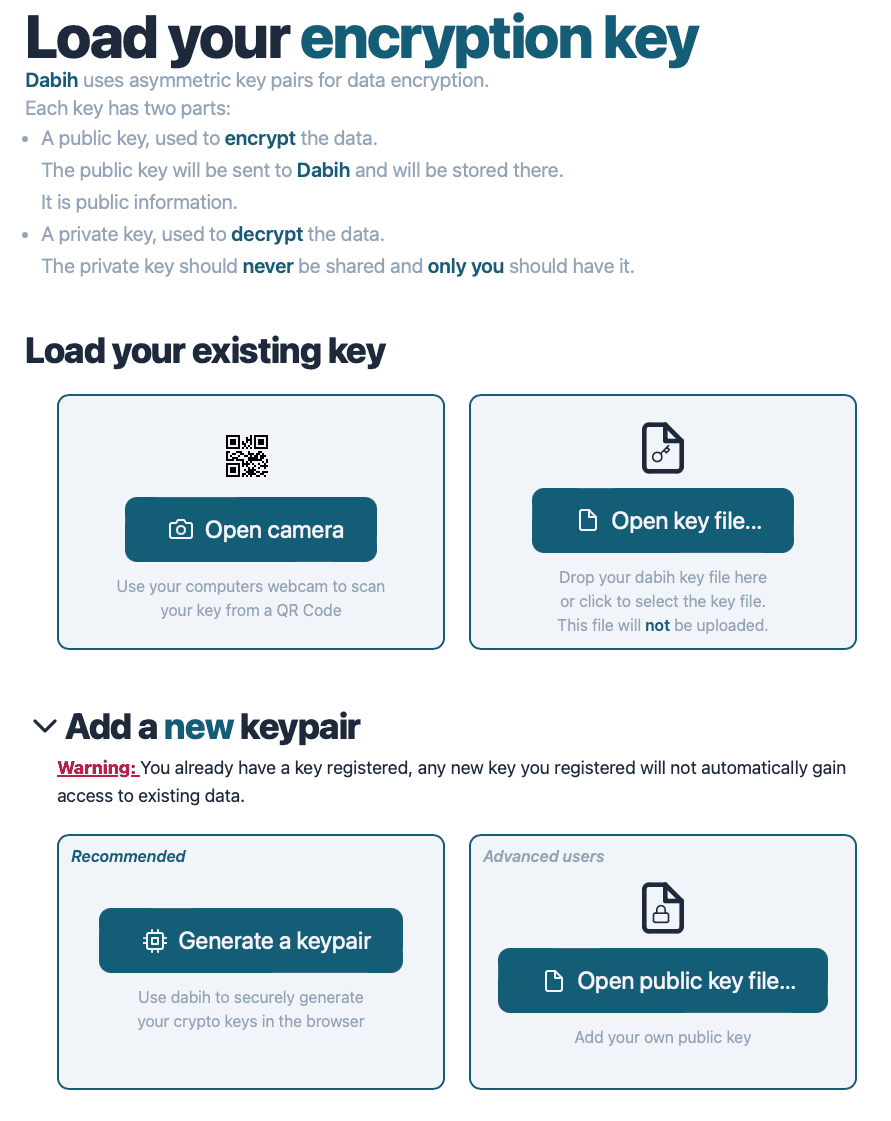
- Keep your private key in a safe location
- Wait for an admin to confirm your key.
- Upload and manage your data.
General Concepts
Encryption
-
During file upload the dataset is processed in memory and not written to disk.
-
When the upload starts the server generates a cryptographically strong pseudorandom AES-256-CBC Key (24 Bytes)
-
The client creates “chunks”, sequential byte buffers of the data, each with size 2 MiB
-
For each chunk we again generate a cryptographically strong pseudorandom initialisation vector (iv)
-
The raw chunk data is hashed using SHA-256 and then encrypted using the AES key with the initialisation vector
-
We then create a crc32 checksum of the encrypted chunk.
-
This encrypted chunk is then written to the file system and the iv, hash and checksum written to the database.
-
All the asymmetric keys are RSA Keypairs, with at least 4096 bits.
-
We use RSA with Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP).
-
To prevent key exchange attacks all keys are fingerprinted using a SHA-256 hash.
Institute of functional genomics-Statistical Bioinformatics
©2023 · Version 1.12.14
Contact/Impressum · Privacy Policy · Data Policy · Documentation